|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
2. Class : Ascomycetes (higher fungi)
These are also called sac fungi distinguished
by the following characteristics:
(I) Mycelium with septate hyphae.
(ii) Asexual reproduction by conidia is a common feature. They are produced at the apex of the hyphae called conidiophores.
(iii) Sexual reproduction occurs by producing sac-like structures called asci, each with usually 8 ascospores, produced endogenously.
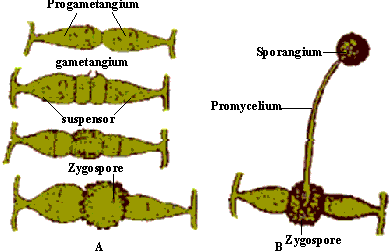
Figure 14.39 Sexual reproduction in Mucor
(iv) Formation of multicellular complex fruiting body
called an ascocarp containing many asci.
(v) Some ascomycetes, like yeast, reproduce by budding
also.
The bodies of ascomycetes may be unicellular as in yeast,
or multicellular and filamentous as in powdery mildew. Ascomycetes include
yeast, powdery mildew, Claviceps, and most of the blue, green and brown
molds.
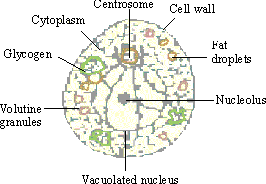
Figure 14.40 Yeast
Reproduction : In most Ascomycetes, asexual reproduction takes place by formation of conidia which are pinched off from the apex of certain specialized hyphae known as conidiophores. e.g. Penicillim
Sexual reproduction takes place by the formation of ascospores within the asci. Some ascomycetes are heterothallic (dissimilar mating types) and other are homothallic (similar mating types). e.g. Claviceps.
Economic importance : Yeast is used for the production
of alcohols in brewery, in production of vitamin B, and for raising bread.
Claviceps is used to extract an alkaloid called ergotin which
is used in medicine. LSD is also extracted from an ergot fungus. Some
ascomycetes like Morchella are edible. Neurospora has been
used recently for genetic and biochemical research. Some ascomycetes cause
severe plant diseases.
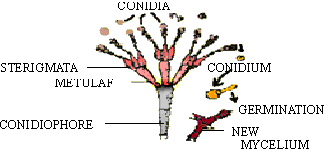
Figure 14.41 Penicillium
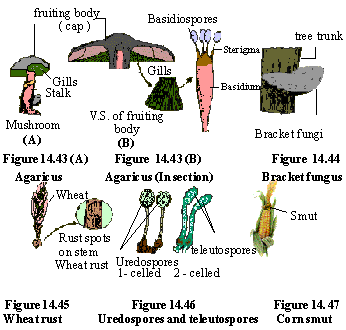
Class: Basidiomycetes (higher fungi)
These are also called club - fungi distinguished
by the following characteristics:
(I) Mycelium with septate hyphae.
(ii) Asexual reproduction is uncommon.
(iii) During sexual reproduction mycelium develops enlarged
reproductive, club-shaped structure called a basidium, hence the
name.
(iv) Each basidium produces 4 basidiospores at
the tip outside (exogenously),unlike ascospores which develop within the
ascus..
(v) In some fungi like mushrooms, a multicellular, complex,
fruiting body called a basidiocarp is formed which is often open,
sometimes closed. (Basidiocarp = basidia bearing body).
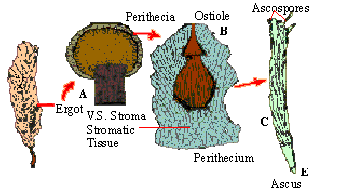
Figure 14.42 Reproduction in Ascomycetes (Claviceps)
Basidiomycetes include large and conspicuous fungi like
mushrooms, toadstools, bracket fungi and puff balls, as well as parasitic
forms like rusts and smuts.
|