|
6.8 General or Ideal Gas Equation
The General or Ideal Gas Equation is obtained by combining relations such as Boyle’s Law, Charles’ Law and Avogadro’s Law.
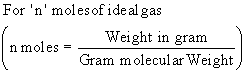
|
PV = nRT where
P- Pressure
V - Volume
R - Constant
T - Temperature
|
This relation is referred to as ’Ideal gas Equation’ as it
holds good only when the gases are behaving as 'ideal' or perfect gases.
R can be calculated as follows :
We know that 1 mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.4 liter at S.T.P. (Standard Temperature & Pressure, i.e 1 atm. pressure and 273 K )
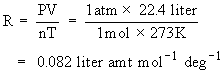
Units of Gas constant R
1) R = 0.082 liter atm deg-1 mol-1
2) R = 8.31 ´ 107 ergs deg-1 mol-1
3) R = 8.31 J deg-1 mol-1
4) R = 2 cal K-1 mol-1
Finally at Glance
|
No. |
Gas Law |
Mathematical expression |
At constant |
|
1. |
Boyle’s |
P1V1 = P2V2 |
Temperature |
|
2. |
Charles |
V1/ V2 = T1/T2 |
Pressure |
|
3. |
Pressure-Temperature |
P1/T1 = P2/T2 |
Volume |
|
4. |
Graham’s |
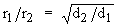
|
Temperature
Pressure |
|
5. |
Gas equation |
PV = nRT |
-- |
**********
[next chapter]
|