|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
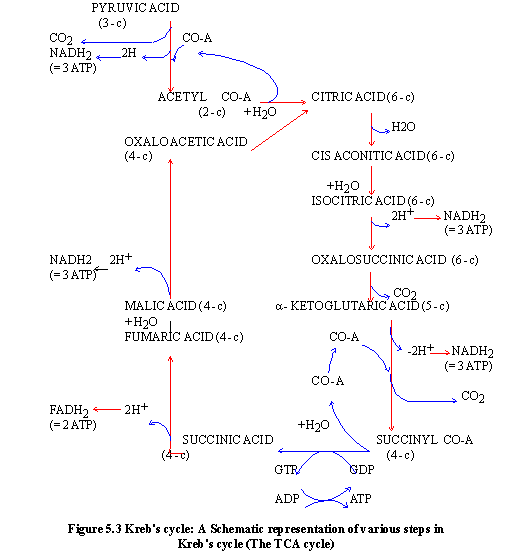
5.4 The T.C.A. Cycle (Tricarboxylic#Acid#Cycle)
The T.C.A. (Tricarboxylic acid) cycle represents
the major set of reactions during Phase-II of the aerobic respiration.
It is also called the citric acid cycle or Kreb’s cycle.
These reactions involve the final breakdown of
pyruvic acid to form the end products of aerobic respiration. The
T.C.A. cycle reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria.
Pyruvic acid is first converted into a 2-C compound called acetyl
co-enzyme-A (Acetyl #Co-A).
Click Here To Enlarge
[next page]
|
Table of Contents
5.0 -
Introduction
5.1 -
Ultrastructure and Functions of Mitochondrion
5.2 -
An Overview of Cellular Respiration
5.3 -
Glycolysis
5.4 -
The T.C.A. Cycle(Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle)
5.5 -
Electron Transport Chain
5.6 -
Fermentation
5.7 -
Significance of Respiration
Chapter
6
|