|
PinkMonkey Online Study Guide-Biology
 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
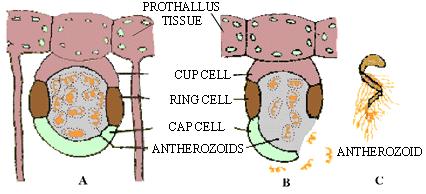
Figure 15.5 (A) Structure of antheridium; (B) Dehiscence of antheridium.
(C) A multiflagellate antherozoid (n)
 Click here to enlarge
Click here to enlarge
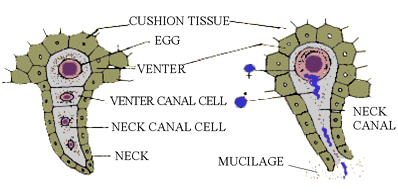
(A) A fully formed archegonium (B) Fertilization
Figure 15.6
Archegonium (Fig. 15.6A). This is the female sex organ. Archegonia develop towards the lower surface of Prothallus in the cushion region.
Each archegonium is sessile with a flask-shaped body.
It is differentiated into basal globular venter and a tube shaped
neck. The venter is embedded in the tissue of cushion but the neck
projects out towards the soil. It is slightly curved. The venter cavity
contains a female gamete called an egg (n) cell and a smaller venter
canal cell. The neck cavity contains one neck canal cell with
two nuclei.
|