|
Composite function : Let f : A ® B and g : B® C be two functions and x be any element of A. Then f(x) Î B. Let y = f(x) Since B is the domain of the function g and C is its co-domain, g(y) Î C. Let z = g (y) then z = g (y) = g[f(x)]Î C. This shows that every element x of set A related to unique element z = g [f(x)] of C. This gives rise to a function from the set A to the set C. This function is called the composite of f and g. It is denoted by ‘g of ’ and we have
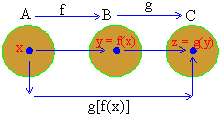
If f : A® B and g : B® C are two functions then the composite of f and g is the function gof : A® C given by
(gof) (x) = g [ f(x) ] 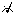 x Î A x Î A
A function ' f ' is such that f (x + p) = f(x) 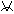 x or f(x) and f(x + p) are both undefined, then p is the period of f : x or f(x) and f(x + p) are both undefined, then p is the period of f :
For example, ' sin e ' has period 2p rad. Since sin (x+2p) = sin x 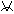 x x
Linear function: f(x) = ax + b, a ¹
0 is called a linear function. The highest degree of
x is 1. It is always one-one onto.
Now we know that a linear equation in y variables
can be expressed in the form:
ax + by + c = 0, a ¹
0 , b ¹ 0. This represents a
straight line. An important part of a straight line is its slope
'm'. It is a number of units the line climbs (or falls) vertically
for each unit of horizontal change from left to right.
Thus slope (m)
= 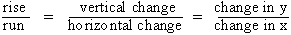
\ m = 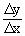 but Dy = y1 - y2
and Dx = x1-x2
but Dy = y1 - y2
and Dx = x1-x2
\ m =
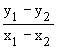 or or 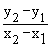
Note that :
-
slope of a horizontal line or any line parallel
to x-axis is always 0, as vertical change remains 0 and horizontal
change remains constant.
-
slope of a vertical line or any line parallel
to y-axis, is said to be undefined, in
other words, it has no slope. Since horizontal change (i.e.
y) remains zero with vertical change (i.e. x) value remains
constant.
-
If q indicates
the inclination of an oblique line with 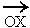 then
slope (m) = tan q. then
slope (m) = tan q.
-
If q is acute,
the line has slope (m) which is positive and if q
is obtuse, line has slope (m) which is
negative.
-
If two straight lines are parallel we have
their slopes being equal, i.e. [ m1 = m2
] and two straight lines are mutually perpendicular,the product
of their slopes equals to -1, i.e. [ m1 ·
m2 = -1 ] Þ m1
= 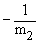
|
Index
Introduction
1.1 Functions And Mapping
1.2 Functions, Their Graphs and Classification
1.3 Rules for Drawing the Graph of a Curve
1.4 Classification of Functions
1.5 Standard Forms for the equation of a straight line
1.6 Circular Function and Trigonometry
Chapter 2
|