Note

In scalar form
F = ma
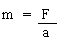
Thus, the ratio of the force applied to the acceleration produced gives us the mass of the object.
Third Law
If an object A exerts a force (called action) on another object B, then the object B exerts equal
and opposite force (called Reaction) on object A.
Note
The terms action and reaction are mutually interchangeable. i.e. force by B on A is action and force by A on B (equal and opposite) reaction.
The action and reaction occur simultaneously.
The action and reaction can never act on the same object.
Friction and Force of Friction
The opposition to the motion of an object moving over the surface of another object, is called friction;
the force arising due to friction is called the force of friction.
The force of friction opposing the motion of an object from rest is called static friction; and the force
of friction opposing the moving object is called Kinetic friction.
These forces of friction possess the following characteristics :
They always act in the opposite direction to motion.
They increase in magnitude upto a certain maximum value. This maximum force is called limiting the force of friction.
The limiting force of friction is independent of the area of contact between the surfaces.
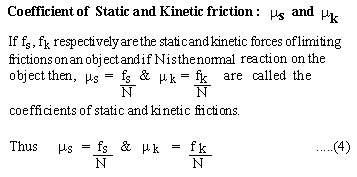
The limiting force of friction is proportional to the normal reaction force.
For the same object, the limiting force of friction is different for different surfaces.
For the same object, the limiting force of friction is different for the same surface, depending upon the lubrication of the surface.
|
Index
3.1 Dynamics of a particle
3.2 Dynamics of a system of particles
3.3 Law of Conservation of Momentum
Chapter 4
|


