|
Example The mean of a certain number of
observations is 40. If two or more items with values 50 and 64 are
added to this data, the mean rises to 42. Find the number of items
in the original data.
Solution:
Let 'n' be the number of observations whose mean 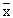 = 40. = 40.
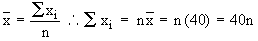 total of n values. total of n values.
Two more items of values 50 and 64 are added therefore, total of (n + 2) values :
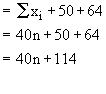
Now new mean is 42.
\ New 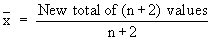
\
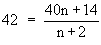
\ 42n + 84 = 40n + 114
\ 2n = 30
\ n = 15
Therefore, the number of items in the original data = 15.
Example The sum of deviations of a certain
numbers of observations measured from 4 is 72 and the sum of deviations
of observations measured from 7 is -3. Find the number of observations
and their mean.
Solution:
Let 'n' be the required number of observations 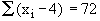 , therefore, , therefore, 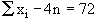
......Note 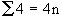 and
and 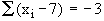 therefore,
therefore,
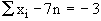 Subtracting the two equations we get, Subtracting the two equations we get,
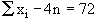
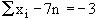
(-) (+) (+)
3n=75
\ n
= 25
Putting n = 25 in 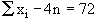 , we get , we get
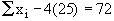
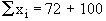
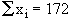
Now Mean is given by 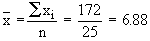
|