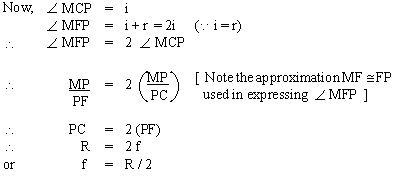|
Curved Spherical Mirrors
Concave Mirror
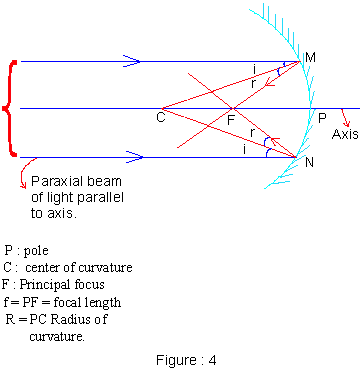
The paraxial (close to axis) beam of light is parallel to the axis, after reflection converges at F; when the Laws of reflection are applied to small parts at M and N, they are considered as flat or plane surfaces.
Image formation in concave mirror The ray diagram will be drawn as follows : (i) A ray incident and parallel to axis will reflect through
focus.
|
16.1 Laws
of Reflection at plane surfaces Follow @Pinkmonkey_com  |