|
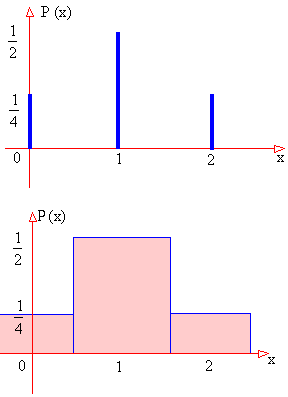
The probability graph can be obtained by using a bar chart as shown
in figure 1 or a Histogram as shown in figure 2.
Total of probabilities of discrete random variables :
As you have noted from the probability distribution table or from
the bar chart (in which the sum of ordinates i.e. heights of bar is
1) and from the Histogram (in which sum of the rectangular area is
1), the sum (total) of probabilities of all values of X always equal
to 1.
Thus, if the random variable X = X1, X2
, X3, ......Xi , ......Xn and Xi
each is associated with a number Pi i.e. X1
with P1, X2 with P2 ......., Xn
= Pn. Then Pi is called probabilities of Xi
and is denoted by P (Xi ) or simply P(X) which satisfies
(1) P (Xi) > 0
(2) 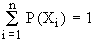 then P (Xi ) or P(X) is called the probability mass function of the discrete random variable X. then P (Xi ) or P(X) is called the probability mass function of the discrete random variable X.
i.e. X
X1 X2
X3 ......... Xn
P(X) P1 P2 P3 ......... Pn
Mathematical Expression of a discrete random variable
If X = xi is a discrete random variable.
Taking X = x1, x2, ....... , xn with respective probabilities
Pi = P1 , P2 , ........., Pn then
The mathematical expression of X is denoted by E(X) and denoted by,
E(X) = P1X1 + P2 X2
+ ...... + Pn Xn = 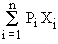
Mean and Standard deviation : If the random
variable X, assumes the values x1, x2, ...
, xn with associated probabilities as P1 ,
P2 , ......... Pn respectively then ,
Mean ( X or m) = 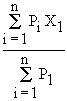
[next page]
|