|
4.5 Factorization and Defactorization
Factorization (Sums or Differences into Products)
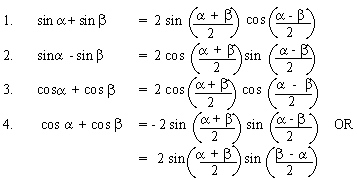
Defactorization (Products into Sums or Differences)
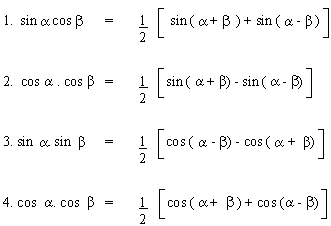
Note : These identites are
valid for both degree and radian measure whenever both sides are
defined.
EXAMPLE 1 Verify that sin C
+ sin D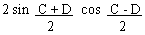
Solution
We know that sin (a
+ b) = sin a
cos b + cos a
sin b ............(i)
sin (a - b)
= sin a cos b
- cos a sin b
.............(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii) we get,
sin (a + b
) + sin (a - b
) = 2 sin a cos b
.............(iii)
substracting (ii) from (i) we get
sin (a + b
) - sin ( a - b
) = 2 cos a cos b
............(iv)
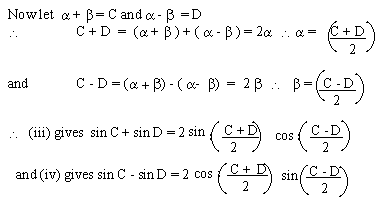
EXAMPLE 2
Verify that sin 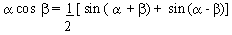
Solution
We know that sin (a
+ b ) = sin a
cos b + cos a
. sin b ......(i)
and sin ( a - b)
= sin a cos b
- cos a sin b
......(ii)
Adding (i) and (ii) we get
sin ( a + b)
+ sin ( a - b
) = 2 sin a . cos b
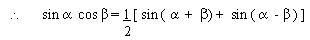
EXAMPLE 3 Prove that 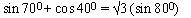
Solution
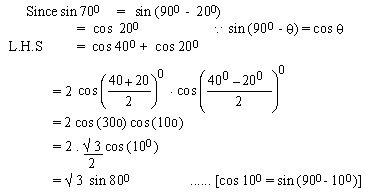
EXAMPLE 4 Write cos 7x cos
4x as a sum.
Solution
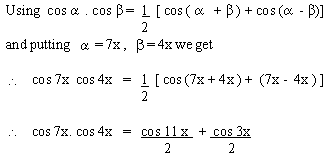
EXAMPLE 5 Write the difference
cos 2 a - cos 8a
as a product.
Solution:
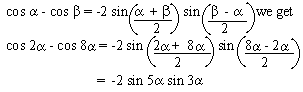
EXAMPLE 6 Find the exact value of sin 75
0 + sin 150
Solution :
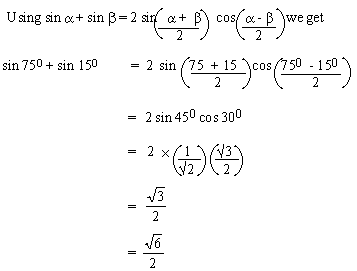
EXAMPLE 7 Prove that sin 7A
+ sin 3A = cot 2A
Solution :
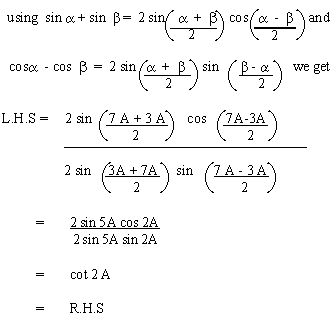
EXAMPLE 8 If sin a
+ sin 3 a = cos a
+ cos 3 a then prove that, either tan 2a
= 1 or cos a = 0
Solution: sin a
+ sin 3a = cos a
+ cos 3a ......(Given)
\ 2 sin 2a
cos a = 2 cos 2a
cos a
\ sin 2a
cos a - cos a
. cos 2a = 0
\ (sin 2a
- cos 2a) cos a
= 0
\ either i) sin 2a
- cos 2a = 0 or ii) cos a
=0
\ i) sin 2a
= cos 2a \
tan 2a = 1
ii) cos a = 0
EXAMPLE 9 Find the value of
cos 520 + cos 680 + cos 1720
Solution:
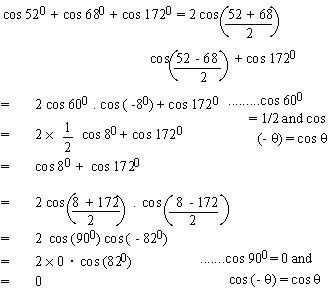
EXAMPLE 10 Express as a sum
or difference sin 55 0 sin 400
Solution: Using sin a
sin B = 1/2 [ cos ( a
- b ) - cos ( a
+ b ) ] we get,
\ sin 550
sin 400 = 1/2 [ cos ( 56 0 - 400)
- cos ( 550 + 400)]
= 1/2 [cos 150 - cos 950]
EXAMPLE 11 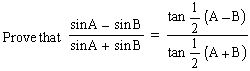 Solution :
Solution :
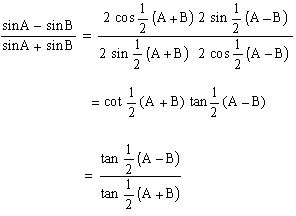
EXAMPLE 12 cos 3x sin2x =
1 /16 (2 cos x - cos 3x - cos 5x)
Solution: cos3x
. sin2x = (sin x cos x ) 2cos x
= (1/2 x 2 sin x cos x )2 cos x
= 1/4 (2 sin x cos x )2 cos x
= 1/4 (sin 2x )2 (cos x) ....(\
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x)
= 1/4 ( sin 2x ) ( sin 2x cos x )
= 1/4 ( sin 2 x ) [1/2 ( sin 3x + sin x)] ....sin
a cos b
= 1/2[sin (a +b
)cos( a - b
)]
= 1/8 [ sin 3x sin 2x + sin 2x sin x ]
= 1/8 [ 1/2 (cos x - cos 5x ) + 1/2 (cos x - cos
3x )]
= 1/16 [ 2 cos x - cos 3x - cos 5x ]
EXAMPLE 13 Simplify cos 3x
cos 2x cos x
Solution :
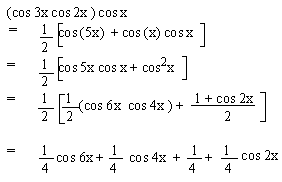
EXAMPLE 14 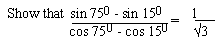
Solution:
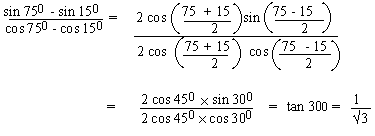
EXAMPLE 15 Find acute angles
A and B satisfying
i) cot ( A + B) = 1 , cosec (A - B) = 2 ii) sec
A cot B - sec A - 2 cot B + 2 = 0
Solution:
i) \ cot ( A+ B) =
1
\ tan ( A+ B) = 1
\ (A + B) = 450
and
\ cosec (A - B) =
2
\ sin ( A - B) = 1/2
\ A - B = 300
Thus we have A + B = 450 and A - B
= 300 , adding we have 2A= 750
A = 37.50and subtracting we get 2B
= 150
\ B = 7.50
ii) sec A 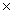 cot B - sec A - 2 cot B + 2 = 0
cot B - sec A - 2 cot B + 2 = 0
\ sec A ( cot B -
1 ) - 2 ( cot B - 1 ) = 0
\ ( sec A - 2 ) (
cot B - 1 ) = 0
\ sec A = 2 or cot
B = 1
\ cos A = 1/2 or tan
B = 1
\ A = 600
or B = 450
[next page]
|