|
8.2 De - Moivre's Theorem
A French Mathematician De' Moivre (1967 - 1974) laid down an important
theorem which gives us the powers of complex numbers.
If 'n' is any real number, then one of the value of (cos q
+ i sin q)n is cos nq
+ i sin nq
For we shall consider the following three cases.
Case (I) n be a positive integer
Consider (cos q + i sin q)n
= (cos q + i sin q)
(cos q + i sin q)
........n times.
= cos (q + q
+ ....n times) + i sin (q + q
+ .....n times)
= cos nq + i sin nq
Take n = 1 , 2, 3, ..... and verify
Case (II) n be a negative number
Let n = - m, m being positive integer
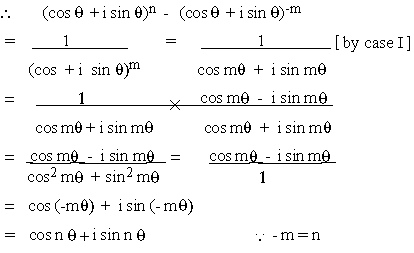
Case III Let n be a fraction, \ n = p /q
Now (cos q/q + i sin q
/ q )q = cos q + i sin q .......[
by (I) and (II)]
\ (cos q +
i sin q)n = (cos q
+ i sin q) p/q
= (cos pq + i sin pq)1/q
= cos ( p/q q) + i sin ( p/ q) q
= cos n q + i sin n q
Hence the theorem is proved for all real numbers.
Remarks
(1) (cos q1 + i sin q2)
(cos q2 + i sin q1) = cos (q1 +
q2) + i sin (q1 + q2)
This can be generalized.
(2) (cos q - i sin q)
n= [ cos ( - q) + i
sin (- q)]n = cos (- nq)
+ i sin (- nq)
= cos n q - i sin n q
(3) 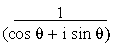 = cos q - i sin q
and
= cos q - i sin q
and 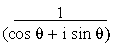 = (cos q + i sin q)
= (cos q + i sin q)
(4) 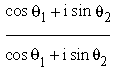 = (cos q1 - q2)
+ i sin ( q1 - q2)
= (cos q1 - q2)
+ i sin ( q1 - q2)
(5) [sin q + i cos q
]n = [ cos (900 - q)
+ i sin (900 - q)]n
= cos n(900 - q) + i sin
n (900 - q)
(6) [ cos q + i sin f
]n ¹cos nq
+ i sin nf
[next page]
|