|
EXAMPLE 4 Prove that (l + j)8+ (l - j)8
= 32
Solution
Now l + j Þ x = 1 and y = 1 ..
(1st - Quad) 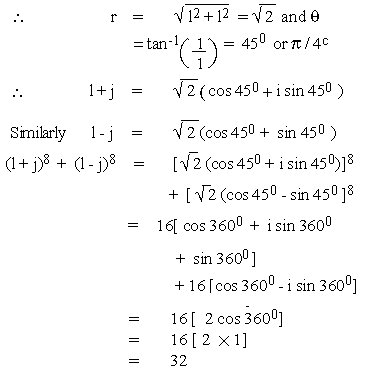
EXAMPLE 5 Prove that (1 + cos q
+ j sin q)n + ( 1 + cos q
- j sin q)n
=
2n + 1 cosn (q / 2) cos (n
q / 2)
Solution
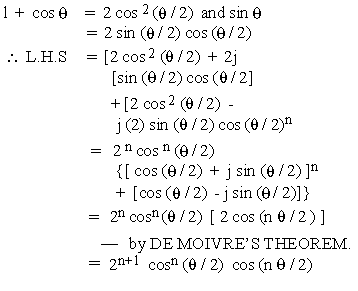
EXAMPLE 6 If P be a real and the complex number 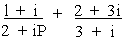 be represented by a point in the Argand's diagram on the line x
= y.
be represented by a point in the Argand's diagram on the line x
= y.
Show that P = 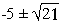
Solution
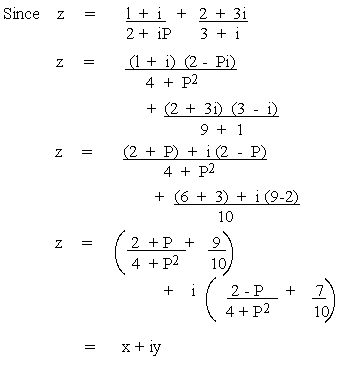
But the point is on the line y = x Þ
x = y
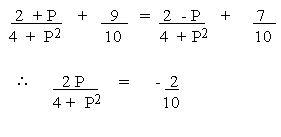
P2 + 10P + 4 = 0 Solving we get P = 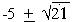
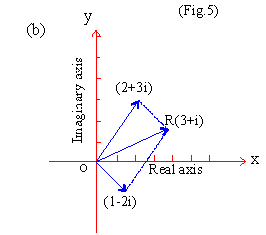
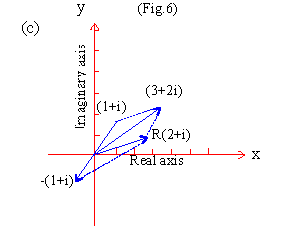
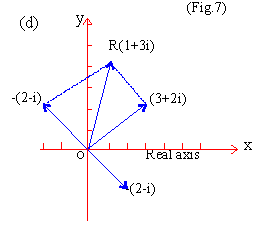
EXAMPLE 7
Perform graphically the following operations
(a) ( 1 + 3i) + (5 + 4i) (b) (2 + 3i) + (l - 2i) (c) (3 + 2i)
- (l + i)
(d) (3 + 2i) - (2 - i)
Solution
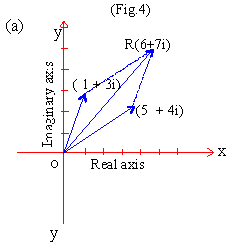
[next page]
|