|
12.2 Conjugate Acid Base Pair
Acid 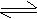 H+ (proton) + Base H+ (proton) + Base
An acid and a base which differ by a proton are said to form a
conjugate acid base pair or the pairs of substances
which can be formed from one another by the gain or loss of protons
are known as conjugate acid base pairs.
Table 16 Conjugate acids and bases.
|
Acid1
+ Base2
|
Acid2 + Base1
|
|
HCl + H2O
HNO3 + H2O
HCN + H2O
HS- + H2O
H2O
+ H2O
|
H3O+ + Cl-
H3O++ NO3
H3O+
+ CN-
H3O+ + S-2
H3O+ + OH-
|
[next page]
|
Index
12.1 -
Lowry and Bronsted Concept
12.2 -
Conjugate Acid Base Pairs
12.3 -
Amphoteric Substance
12.4 -
Lewis Acids and Bases
12.5 -
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
12.6 -
Dissociation
12.7 -
Ostwald's Dilution Law
12.8 -
Hydrogen Ion Concentration : pH
12.9 -
Polyprotic Acids
12.10 -
Salts
12.11 -
Methods of Preparation of Salts
12.12 -
Properties of Salts
Chapter
13
|