|
5.3 Range
In any statistical series, the difference between the largest and the smallest values is called as the range.
Thus Range (R) = L - S 
Coefficient of Range :
The relative measure of the range. It is used in the comparative
study of the dispersion co-efficient of Range = 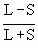
Example ( Individual series ) Find the range and the co-efficient of the range of the following items :
110, 117, 129, 197, 190, 100, 100, 178, 255, 790.
Solution: R
= L - S = 790 - 100 = 690
Co-efficient
of Range = 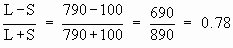
Example (Continuous series ) Find the range and its co-efficient from the following data.
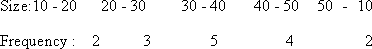
Solution: R = L - S = 100 - 10 = 90
Co-efficient
of range = 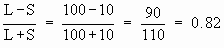
[next page]
|