|
Example 2
Evaluate
1) 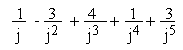
Solution
j2 = -1, j3 = j2 ´
j = - j, j4= (j2)2= (-1)2
= 1 and j5 = j4 ´
j = (1) j = j
then 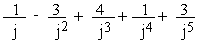
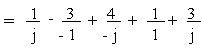
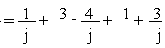 = 4
= 4
Example 3
Perform the indicated operations.
(a) ( 4 - 2i) + (- 6 + 5i) = 4 - 2i - 6 + 5i = (4 - 6) + (-2 +
5) i = -2 + 3i
(b) (-7 - 3i) - (2 - 4i) = (-7 -2) + (-3 + 4) i = -9 + i
(c) (3 - 2i) (1 + 3i) = 3 (1 + 3i) - 2i (1 + 3i) = 3 + 9i - 2i -
6i2 = 3 + 9i - 2i + 6 = 9 + 7i
(d) 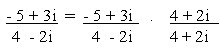
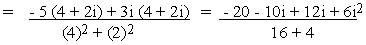
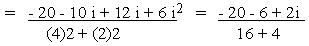
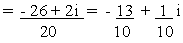
Example 4
Simplify
a) 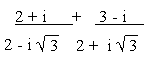
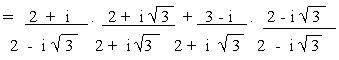
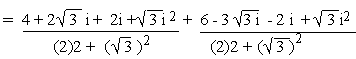
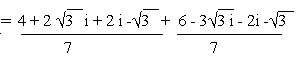
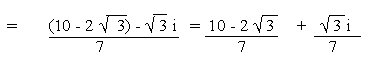
b) 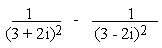
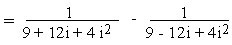
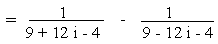
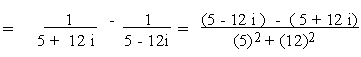
Example 5
Find the real values of 'a' and 'b' if
(a) (a - 2bi) + (-b - 3ai) = 5 +
2i
Solution
(a - b) + (-2b -3a)i = 5 + 2i. Equating the real and imaginary
parts, we get
a - b = 5 ....(1) and - 2b - 3a =2 .......(2) solving we get
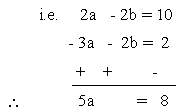 a =
a = 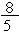 putting a =
putting a =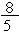 in
in
(1) 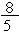 - b = 5
- b = 5
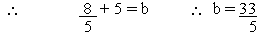
(b) (2 - 3i) (4i + 5) = a + bi
Solution
(2 - 3i) (5 + 4i) = a + bi
\ 10 + 8i - 15i - 12i2
= a + bi
\ (10 + 12) - 7i = a + bi
\ 22 - 7i = a + bi. Equating the real
and imaginary parts we get a = 22 and b = -7
[next page]
|