|
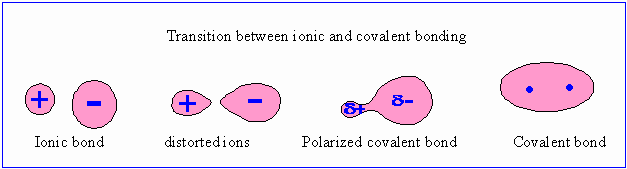
Transition between Ionic and Covalent Bonding :
Chemical reactions and physical measurement support the belief that most chemical compounds are intermediate in character between the purely ionic and the purely covalent.
Ionic bonds are found in compounds between the metals of low ionization potential and non-metals of high electron affinity.
A pure covalent bond is found only in molecules formed from two
identical atoms such as Cl2.
Most compounds fit somewhere between these two extremes.
If two spherical ions of opposite charges are brought together, the positively charged ion attracts and reforms the electron cloud of the anion. The electron cloud of the anion is drawn toward the cation, and, in extreme cases such ion deformation can lead to formation molecules with predominant covalent bonds.
Click here to enlarge
Thus Aluminium chloride is a predominantly covalent material and not pure ionic material.
[next page]
|