| 16.2 Mirrors
Plane Mirror
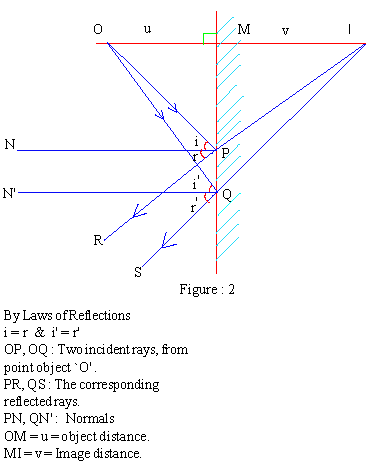
The reflected rays PR and QS diverge from each other, therefore, they are extended backwards to meet at I, the image I is therefore the virtual image behind the mirror. From the geometry of the ray diagram, it is obvious that v = u. The image of a finite sized object in a plane mirror is virtual, erect, laterally inverted, behind the mirror and at same distance as the object. These are obvious consequences of the laws of reflection; these characteristics of the image are illustrated in Fig. 3 |
16.1
Laws of Reflection at plane surfaces Follow @Pinkmonkey_com  |